“Our goal is to explore and gather as much scientific data as possible.”
— Zhang Rongqiao, China’s Chief Tianwen-1 Manager, CNAS
January 7, 2022 Albuquerque, New Mexico – On New Year’s Day 2022, China’s National Space Administration released four new images of its Tianwen-1 Mars mission orbiter taken by released for selfies at about 217,479,917 miles (350 million km) from Earth. On December 31 2021, the Tianwen-1 orbiter deployed a second camera into Mars orbit to get Tianwen-1 selfies in orbit as celebration of so much success by the beginning of 2022.
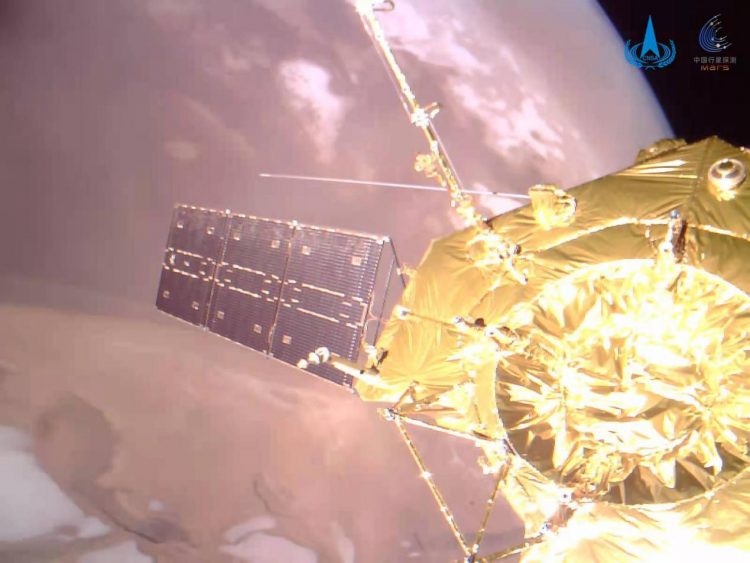
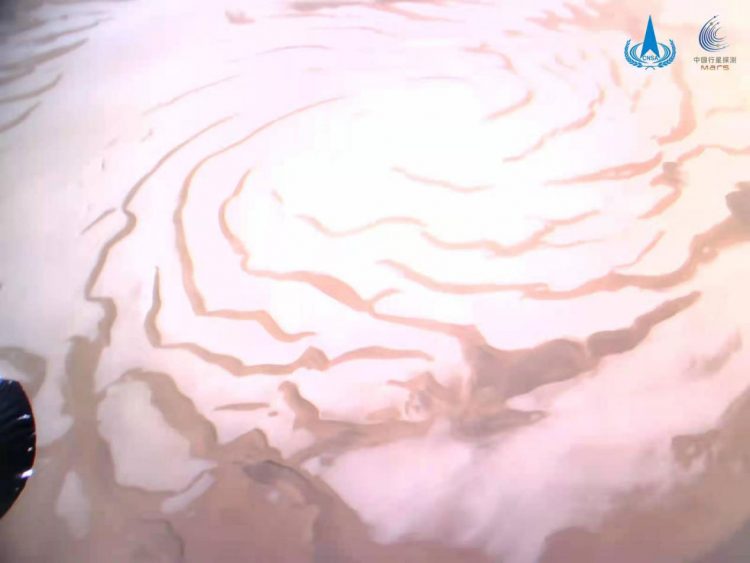
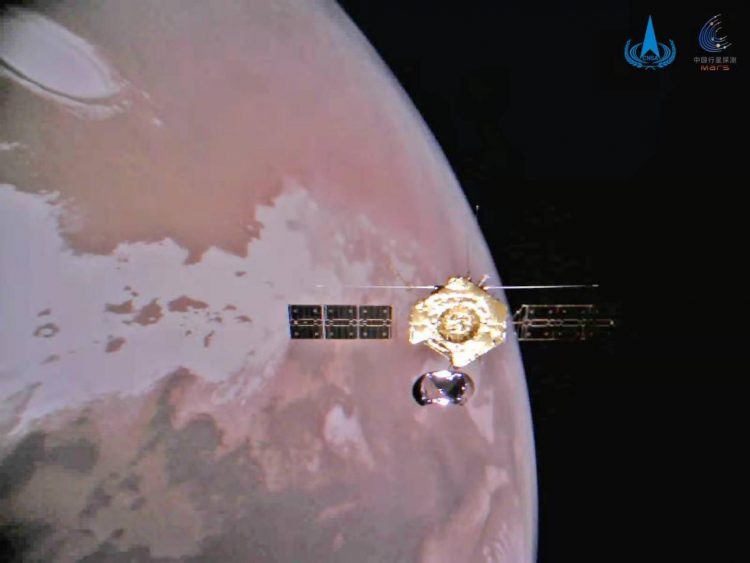


China’s Tianwen-1 Orbiter, Lander, and Rover Reached Mars Orbit February 10, 2021, and Landed May 22, 2021.
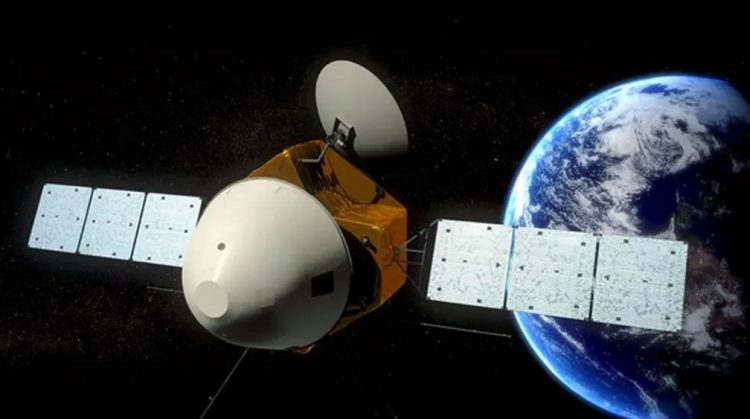

Tianwen-1 was named after an ancient Chinese poem about “questions to heaven.” After reaching orbit around Mars in February 2021, by May 14, 2021, the lander/rover portion of the mission successfully touched down on Mars, making China the third Earth nation to both set down a lander communicating with an orbiter from the Martian surface. Before China’s Tianwen-1, the Soviet Union and the United States were first. And the first five Mars rovers were from the United States.
By Saturday morning, January 1, 2022, the Zhurong rover had traveled more than 4,593 feet (1,400 m) and is still in good condition with power.
This is the CNSA’s first interplanetary mission, as well as its first independent probe to Mars. It’s also a serious test of China’s deep space communications and control technologies. Scientists will study:
— the internal structure of the Martian magnetic field;
— search for evidence of current and past life and produce surface Mars maps of soil composition and water ice distribution;
— study the Martian atmosphere and ionosphere;
— Zhurong will store rock and soil samples on the Martian surface for retrieval by a later sample-return mission in the 2030s while the orbiter will record exactly where Zhurong stored those samples.
The Tianwen-1 mission was the second of three Martian exploration missions launched in July 2020: the United Arab Emirates Space Agency Hope orbiter; then China’s Tianwen 1; followed by NASA’s Mars 2020 mission that landed the Perseverance rover along with the Ingenuity helicopter drone.
Also see:
More Information:
11-01-2018 – Mars: Why It’s A Strange Cloud and Not Volcano Smoke.
Websites:
Emirates Mars Mission: https://www.mbrsc.ae/emirates-mars-mission
American Mars 2020 Mission Perseverance Rover: https://mars.nasa.gov/mars2020/
“China’s daring Tianwen-1 Mars Mission: Everything we know,” C-Net.com, July 20, 2020: https://www.cnet.com/news/chinas-daring-tianwen-1-mars-mission-everything-we-know/
AAAS Science, “Mars mission would put China among space leaders,” June 25, 2020: https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2020/06/mars-mission-would-put-china-among-space-leaders
© 1998 - 2024 by Linda Moulton Howe.
All Rights Reserved.

