— “Those two bright spots are very intriguing. DAWN will resume
taking pictures in the early part of May 2015 ... three times sharper
than the ones we have so far.”
- Marc D. Rayman, Ph.D., Dawn Mission Director
and Chief Engineer, NASA/JPL, Pasadena, California
— “If we discover something like cryovolcanism on Ceres, that would be spectacular because it would be an indicator that there are subsurface reservoirs of water ... and that could make Ceres very astrobiologically important.”
- Mark Sykes, Ph.D., Director, Planetary Science Institute
and NASA Dawn Ceres Mission Scientist
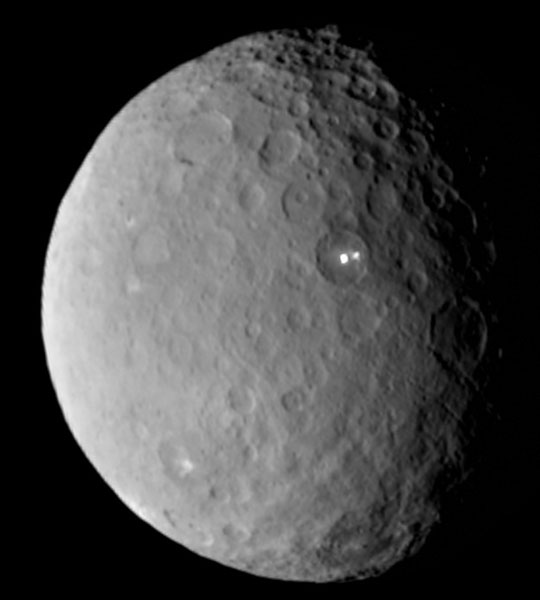

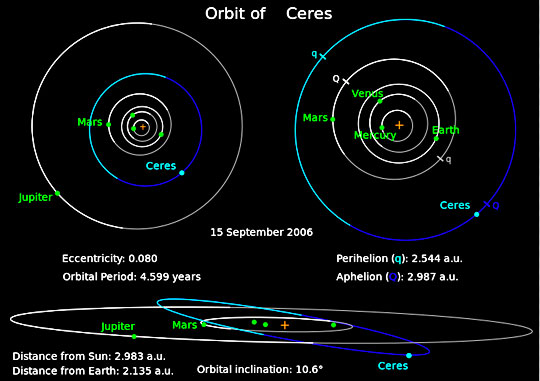
March 27, 2015 Pasadena, California - On February 19, 2015, the NASA/JPL Dawn spacecraft was 28 thousand miles from our solar system's dwarf planet Ceres near the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Ceres is in the small planet category because it is so round. Asteroids are not round. They are jagged rocks. Also, Ceres is only 590 miles in diameter made of 20% water ice with a surface temperature of minus-105 degrees Centigrade. That's a very cold minus-157 degrees Fahrenheit. One of Ceres's many mysteries is what dense ingredients came together at the beginning of this solar system that would have enough mass to form such a small, round ball that might even have a thin atmosphere?
Click here to subscribe and get instant access to read this report.
Click here to check your existing subscription status.
Existing members, login below:
© 1998 - 2025 by Linda Moulton Howe.
All Rights Reserved.

